Configuration
In this topic:
•DIP2: Clock source configuration
•J6 - J15: Trace port configuration
•P2: Power supply configuration
•J4 and J5: GND connection points
|
For a detailed visual presentation of the hardware setup and configuration, refer to: |
DIP1: Target reset configuration
DIP switch DIP1 connects the Emulation Adapter reset line and the target reset line and is on (position next to the white dot) by default. The Emulation Adapter also features a Reset push button (SW1).
If having problems establishing the initial debug session with the Emulation Adapter, adjust the DIP switch DIP1 to the off position (position away from the white dot) and try again.
DIP2: Clock source configuration

DIP2 switch selects the clock source for the emulation device. The Emulation Adapter is delivered with DIP2 in the default position, closer to Pin marking 1.
The default position selects the crystal circuit oscillator on the target board.
To select the crystal circuit oscillator on the Emulation Adapter (Q1 socket), set:
1. The DIP2 switch away from Pin 1 marking.
2. Insert the crystal circuit delivered with the Emulation Adapter into the Q1 socket.
|
The Emulation Adapter may not operate when the target board’s crystal circuit is used as the clock source. A typical design guideline is that the crystal should be as close as possible to the SoC. The target crystal might not oscillate in conjunction with the Emulation Adapter since the clock lines between the target crystal and the emulation device on the Emulation Adapter become too long, thus affecting the impedance of the crystal circuit. |
|
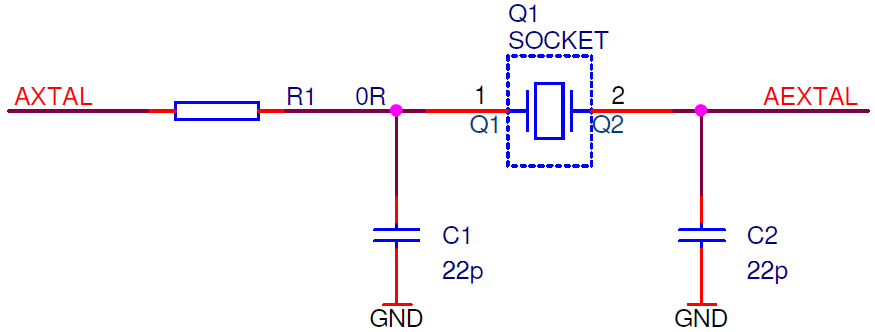
Separately packed 16 MHz crystal can be used as a 16 MHz external clock (XOSC) source to the emulation device. If a different clock frequency is required, insert an adequate crystal into the Q1 socket and replace C1 (default 22 pF populated) and C2 (default 22 pF populated) accordingly. Crystal socket Q1 is by default not populated (NP). |
Crystal socket Q1 schematics below:
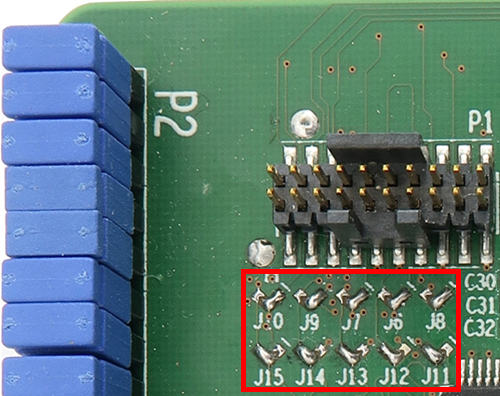
J6 - J15: Trace port configuration
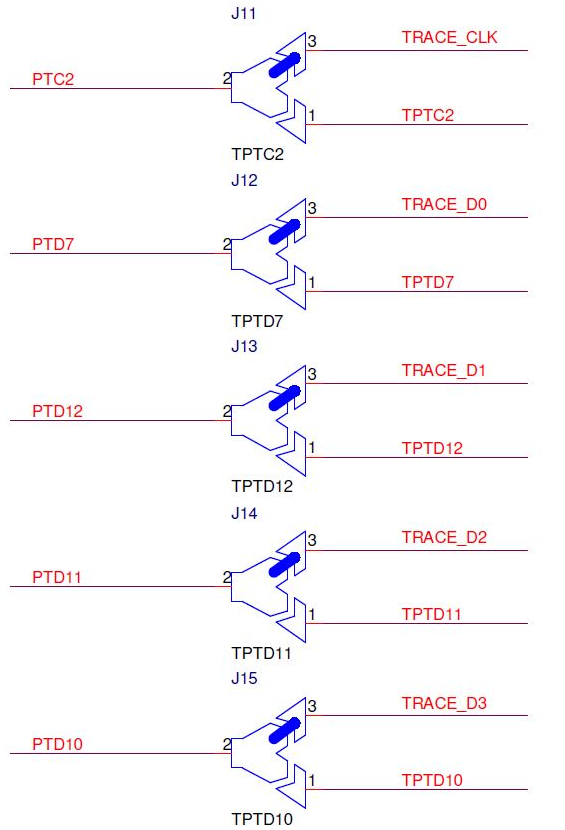
Soldered jumpers are placed by default to connect Arm CoreSight 20 connector trace signals to fast trace pins:
•TRACE_CLK - PTC2
•TRACE_D0 - PTD7
•TRACE_D1 - PTD12
•TRACE_D2 - PTD11
•TRACE_D3 - PTD10
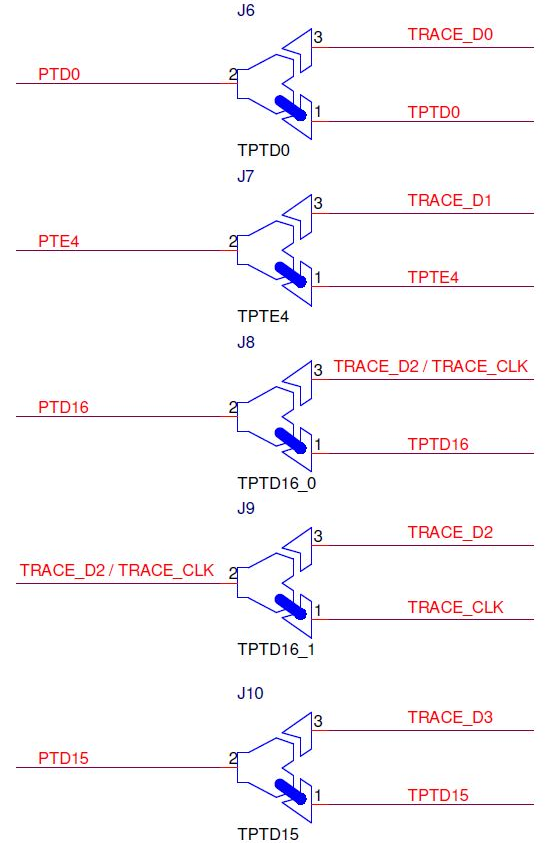
If fast trace pins (PTC2, PTD7, PTD12, PTD11, PTD10) on a target board are used for other functionality purpose than trace, the Emulation Adapter allows connecting trace signals to alternate ports through solder jumpers:
•TRACE_CLK - PTD16
•TRACE_D0 - PTD0
•TRACE_D1 - PTE14
•TRACE_D2 - PTD16
•TRACE_D3 - PTD15
Note that PTD16 can operate either as TRACE_CLK or TRACE_D2. Use of alternate ports decrease the performance of the trace interface since output drivers on these ports are slower.
It's recommended to contact TASKING for assistance if the default trace configuration has to be changed.
Soldered jumpers J6-J15 on the Emulation Adapter in the image below:
winIDEA configuration
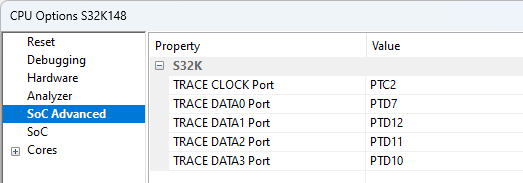
Configure winIDEA accordingly depending on which ports are connected to the physical trace interface. Open Hardware | CPU Options | SoC Advanced. Depending on the target board configuration, set:
•TRACE CLOCK Port to PTC2 (alternative PTD16)
•TRACE DATA0 Port to PTD7 (alternative PTD0)
•TRACE DATA1 Port to PTD12 (alternative PTE4)
•TRACE DATA2 Port to PTD11 (alternative PTD16)
•TRACE DATA3 Port to PTD10 (alternative PTD15)
P2: Power supply configuration
Power supply of the Emulation Adapter is configured via the unshrouded 26-pin 2.54 mm header (P2).
Signal direction |
Signal |
Pin |
Pin |
Signal |
Signal direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Target board |
TVDD |
1 |
2 |
VDD |
Emulation device |
Target board |
TVREFH |
3 |
4 |
VREFH |
Emulation device |
Not Connected |
NC |
5 |
6 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
7 |
8 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
9 |
10 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
11 |
12 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
13 |
14 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
15 |
16 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
17 |
18 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Not Connected |
NC |
19 |
20 |
NC |
Not Connected |
Ground |
GND |
21 |
22 |
GND |
Ground |
Ground |
GND |
23 |
24 |
GND |
Ground |
Ground |
GND |
25 |
26 |
KEY |
|
P2 Signal description
Signal Direction is described from the BlueBox perspective.
By default, all jumpers are set to connect your target power supply to the microcontroller residing on the Emulation Adapter. Only pins 1-2 and 3-4 must be bridged, but for the convenience and ease of use, all jumpers are set, except for pins 25-26.
Pin 26 is the polarizer key pin preventing incorrect connection of the IEA-PS Power converter, when being plugged in.
If a different power source is used (e.g., a Standalone operation), remove all jumpers and apply 3V3 or 5V to:
•VDD (pin 2)
•VREFH (pin 4)
Enclosed Power supply package (Power converter and Power adapter) simply plugs into the P2 header row, providing the necessary power supply for Emulation Adapter operation. LED1 indicates if power is supplied to the Emulation Adapter.
Refer to the microcontroller documentation for more details about power voltage designations.
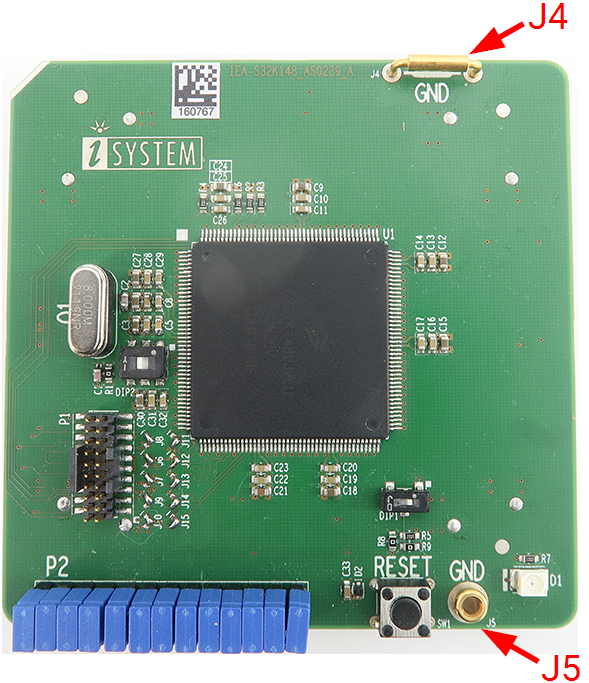
J4 and J5: GND connection points
In case a good ground connection is required, connection points bridge J4 and pin J5 provide easy access to the Emulation Adapter's GND potential.
Connectors
|
Be aware that debug and trace signals from the Emulation Adapter superset device are not connected to the target board. They are exposed only to the connectors on the Emulation adapter. |
P1: CoreSight 20 connector
CoreSight 20 connector P1 exposes debug and trace signals and has the following pinout on the Emulation Adapter side:
Signal Direction |
Signal Description |
Signal |
Pin |
Pin |
Signal |
Signal Description |
Signal Direction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
I |
Reference Voltage |
Vref |
1 |
2 |
SWDIO/TMS |
SWD/JTAG |
I/O / O |
|
Ground |
GND |
3 |
4 |
SWCLK/TCK |
SWD/JTAG |
O |
|
Ground |
GND |
5 |
6 |
SWO/TDO |
SWD/JTAG |
I |
|
Not Connected |
KEY |
7 |
8 |
NC/TDI |
Not Connected / JTAG |
O |
|
Ground |
GND |
9 |
10 |
nRESET |
Reset |
I/O |
|
Reference Voltage / Ground |
NC_CAPGND |
11 |
12 |
TRACECLK |
Trace Clock |
I |
|
Reference Voltage / Ground |
NC_CAPGND |
13 |
14 |
TRACEDATA[0] |
Trace Data |
I |
|
Ground |
GND |
15 |
16 |
TRACEDATA[1] |
Trace Data |
I |
|
Ground |
GND |
17 |
18 |
TRACEDATA[2] |
Trace Data |
I |
|
Ground |
GND |
19 |
20 |
TRACEDATA[3] |
Trace Data |
I |
20-pin ARM CoreSight pinout
Signal Direction is described from the BlueBox perspective.
Connectors P3, P4, P5 and P6 on the bottom side of the Emulation Adapter expose all emulation device signals toward the Conversion board, through which the Emulation Adapter adapts to different pin count packages.
Power supply
Use the enclosed IEA-PS Emulation Adapter Power converter and adapter. A Power supply package, which is delivered with the Emulation Adapter, is required when:
•The Emulation Adapter is used as a standalone device.
•The target board doesn’t provide an accurate supply voltage.
•The target board doesn’t provide sufficient current for the Emulation Adapter operation.
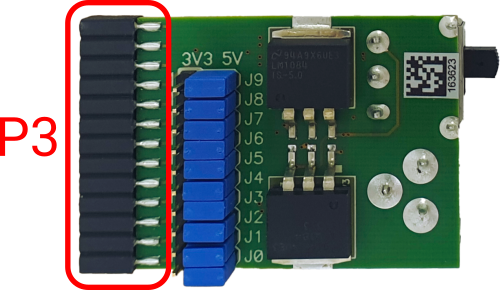
The Power converter can supply either 3.3 V or 5 V. The array of jumpers J0–J9 selects 3.3 V or 5 V voltage on the P3 connector, which connects to the Emulation Adapter.
Signal |
Pin |
Pin |
Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
NC |
1 |
2 |
J0 |
NC |
3 |
4 |
J1 |
NC |
5 |
6 |
J2 |
NC |
7 |
8 |
J3 |
NC |
9 |
10 |
J4 |
NC |
11 |
12 |
J5 |
NC |
13 |
14 |
J6 |
NC |
15 |
16 |
J7 |
NC |
17 |
18 |
J8 |
NC |
19 |
20 |
J9 |
GND |
21 |
22 |
GND |
GND |
23 |
24 |
GND |
GND |
25 |
26 |
KEY |
P3 connector and J0–J9 jumper correlation table
For example, when J2 is in the 3V3 position, it supplies 3.3 V to pin 6 of the P3 connector. When J2 is in the 5V position, it supplies 5 V to pin 6 of the P3 connector pin.
|
Be careful not to supply 5 V to the microcontroller power supply pin, which has declared a maximum voltage 3.3 V! Refer to the microcontroller documentation for detailed information on power supply. |
P3 connector on the Power Supply board
External power supply requirements:
Min Voltage |
Max Voltage |
Min Power |
|
|---|---|---|---|
8 V |
12 V |
5 W |
Clock source
If the target’s crystal circuit microcontroller oscillator (if available) is not an adequate clock source, insert the appropriate crystal into the Q1 socket, replace the default 22pF C1 and C2 capacitors when necessary, and DIP switch DIP2 to position away from the white dot.