Modify memory content
In this tutorial, you will learn:
•display and manage memory content directly of via Fill dialog,
•make modifications to memory contents,
•track changes.
Memory window is best suited for a raw view of the CPU memory. It allows you to view memory contents, search memory for specific pattern, modify memory content directly in the window, modify memory content via Fill for larger memory areas, and dump memory contents to a file. Like Real-Time Watch, Real-time access can impact real-time performance of the application code and depends on the MCU debug interface performance.
You can easily drag and drop a register from Disassembly into the Memory Window to display memory from register value.
Modify memory content
Memory contents can be modified directly in the window. This approach is recommended for modifying smaller portions of the memory (e.g. arrays).
|
Open the Memory via View | Debug | Memory | Create. |

|
Make sure memory area is visible. |
Debug session must be established and memory area must be memory mapped.
|
Select a location. |
With clicking, a block caret will appear covering the selected location.
|
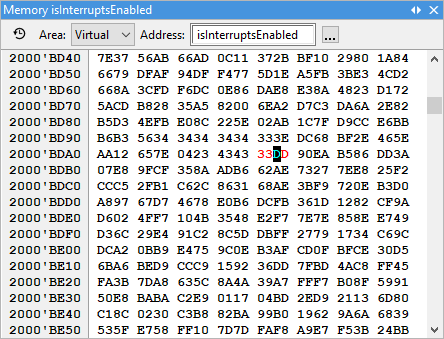
Enter the new value. |
When entering value in the ASCII display area or when using binary or hexadecimal display types, individual digits can be modified directly.
In decimal (float and integer) display mode, entering a new value automatically opens the Fill dialog.
|
If the memory does not change, the CPU might have problems with write access to that location. |
Modify memory content via Fill
Memory contents can be modified via Memory Fill dialog.
|
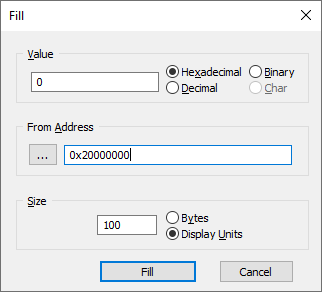
Right click in the window and select Fill. |
|
Enter the new Value. |
|
Define From Address. |
This is initially set to the address that was selected at the time the dialog opened, and can also be changed to an alternate memory location.
|
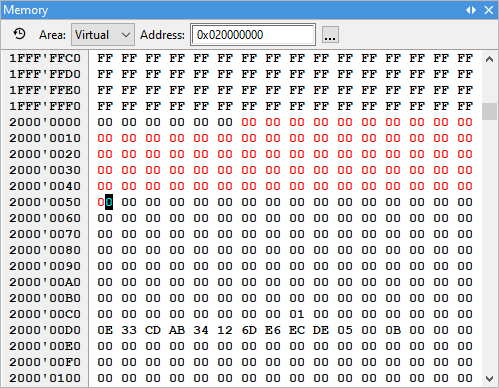
Define Size. |
Used to determine how many locations will be filled with the specified value.
The Bytes/Display Units setting should be set as follows:
•Bytes - Should be selected to fill a certain number of consecutive bytes.
•Display Units - Should be selected to fill a desired number of data type locations. For example: if you are currently displaying 4 byte values, here we would set the next 10 4-byte locations to ‘123’.
More resources
•Memory in detail