Console
In this topic:
•Context-aware auto-suggestions
•Commands case-sensitivity and abbreviations
Introduction
The Console window allows you to issue winIDEA commands through an interactive command line interface. Console window is available also in Visual Studio Code Extension.
You can open the window via View | Workspace | Console or using the shortcut CTRL + SHIFT + C.
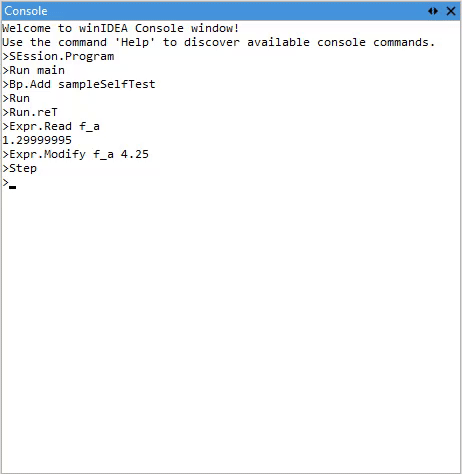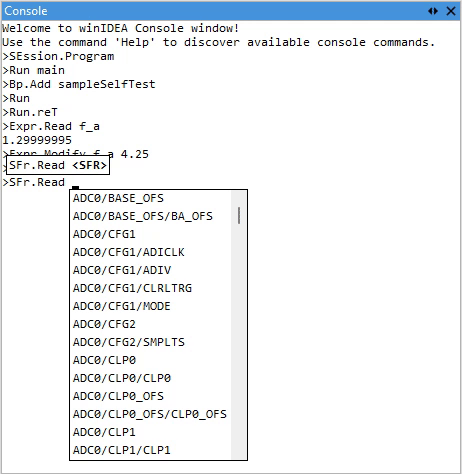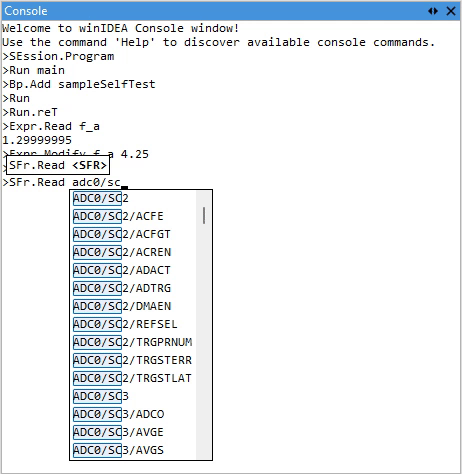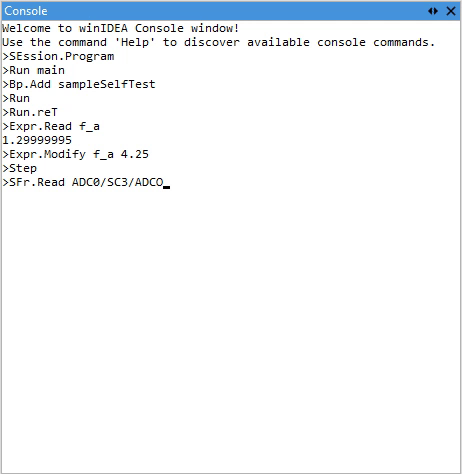
Context-aware auto-suggestions
As you type, an autosuggestion window appears, displaying a list of matching commands. Once a command is selected, the autosuggestion system provides inline hints for the expected argument types and continues to assist as you enter arguments.
Depending on the argument type, auto-suggestions offer auto-completion for:
•SFRs (Special Function Registers) - Based on the connected MCU
•Project files - Filtered according to project structure
•Symbols - Derived from the active Debug Session
This dynamic behavior adapts to the current context, helping you quickly construct valid commands without needing to memorize syntax or symbol names.
For additional details about any command, use the help command at any time.
Controls and shortcuts
Control |
Description |
|---|---|
CTRL + SHIFT + C |
Open the console or place focus on the console. |
CTRL + C, CTRL + V |
Copy text from the console / paste text to the console edit line. |
ESC |
Clear console input, or clear selection, or hide auto-suggestions list (if displayed). |
UP / DOWN |
Navigate through command history, or through auto-suggestions (if displayed). |
ENTER |
Apply autosuggestion to the edit line. |
ENTER |
Execute the command written on the edit line. |
CLS / CLEAR |
Clear the console window. |
HIST, HISTory |
Show the command history. |
H, Help |
Show the console help. |
Commands case-sensitivity and abbreviations
Console commands are case insensitive (use of capitalized letters is optional), and allow abbreviations. Abbreviations are specified by the capitalized letters in the command name. If the command contains a dot, the dot must also be part of the abbreviation. In order for the command name to be recognized, users must enter all subparts of the command by their full or abbreviated form.
For example, these are some of valid entries for the command SEssion.Program:
•Case insensitive: session.program
•First part abbreviated: se.program
•Second part abbreviated: session.p
•Full command abbreviated: se.p
Available commands
Commands are divided into the following categories:
Breakpoints
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Add breakpoint |
|
The command is used to set breakpoints at specified memory addresses or functions |
Set a breakpoint at the function main:
Set two breakpoints: one at the function main and another at memory address 0x2000:
|
||||
Delete breakpoint |
|
The command removes previously set breakpoints. If no arguments are provided, all breakpoints will be deleted. |
Delete all breakpoints:
Delete the breakpoint set at the function main:
Delete the breakpoint at memory address 0x4000 and the breakpoint at function f2:
|
||||
Enable breakpoint |
|
The command enables previously set breakpoints. If no arguments are provided, all breakpoints will be enabled. |
Enable all breakpoints:
Enable the breakpoint set at the function main:
Enable the breakpoint at memory address 0x4000 and the breakpoint at the function f2:
|
||||
Disable breakpoint |
|
The command disables previously set breakpoints. If no arguments are provided, all breakpoints will be disabled. |
Disable all breakpoints:
Disable the breakpoint at the function main:
Disable the breakpoint at memory address 0x4000 and the breakpoint at the function f2:
|
||||
Reapply breakpoints |
|
The command reapplies all currently active breakpoints. |
/ |
||||
Reset breakpoint pass counters |
|
The command resets pass counters of conditional breakpoints to zero. |
/ |
Run control
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Stop |
|
The command stops the program execution. |
/ |
||||
Run, Run until |
|
The command starts the program execution. If a symbol or memory address is specified, the execution will continue until it reaches the given target. |
Start the program execution:
Run the program until it reaches the function main:
Run the program until it reaches memory address 0x4000:
|
||||
Run until return |
|
The command starts the program execution and continues until the current function exits. |
Run the program until the current function exits:
|
||||
Show execution point |
|
The command shows the current point of execution in the editor. |
/ |
||||
Debug Snapshot |
|
The command performs a Debug Snapshot, which shows the application’s state while it’s running. |
/ |
||||
Focus Process |
|
The command is used to focus on a specific Process. If an SMP core is provided, the command will focus on the specified core. |
Focus on the Process running on Core 0:
Focus on the specified SMP core (A53_1):
|
||||
Step |
|
The command steps into the next statement or function. If no argument is provided, the debugger will execute a single step. If a numerical value (count) is specified, the program will step count number of times. |
Execute one step:
Execute five steps:
|
||||
Step over |
|
The command steps over the next statement or function call. This means the debugger will execute the current statement and move to the next one without entering function calls. |
/ |
Session management
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Begin Session - Program |
|
The command initializes a new Debug Session, starts emulation (HAR) on all SoCs, and programs them with the target code. |
/ |
|
Begin Session - Reset |
|
The command Initializes a new Debug Session and starts emulation (HAR) on all System on Chips (SoCs). |
/ |
|
Begin Session - Attach |
|
The command Initializes a new Debug Session and attaches to all System on Chips (SoCs) that are configured to attach on session start. |
/ |
|
Begin Session - Prepare |
|
The command Initializes a new Debug Session without attaching to any SoC. |
/ |
|
End Session |
|
The command ends the Debug Session (detaches from all SoCs). |
/ |
SoC control
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
Reset SoC |
|
The command resets the SoC. |
/ |
|
Attach to SoC |
|
The command attaches to the SoC. |
/ |
|
Detach from SoC |
|
The command detaches from the SoC. |
/ |
Core Register and SFR access
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Read SFR |
|
The command retrieves and prints the value of a SFR that is identified by path (<SFR>). |
Read the SFR identified by the path ADC0/CFG1/MODE:
|
|||
Modify SFR |
|
The command modifies the value of a SFR that is identified by path (<SFR>) with a new value (<Value>). |
Write the value 0x3 to the SFR identified by the path ADC0/CFG1/MODE:
|
|||
Read Core Register |
|
The command retrieves and prints the value of a SFR that is identified by path (<CoreRegister>). If no argument is given, it reads all registers. |
Read Core Register R12:
Read all Core Registers:
|
|||
Modify Core Register |
|
The command modifies the value of a Core Register (<CoreRegister>) with a new value (<Value>). |
Write the value 0x15 to Core Register R13:
|
Memory and expressions
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Write memory to an address |
|
The command is used to specify a memory address where the value(s) should be written. |
Write two bytes (0xab, 0xcd) to address 0x100:
|
|||
Write memory to an address range from Address1 to Address2 (inclusive of both borders) |
|
The command is used to specify a range of addresses (inclusive of both borders) where the value(s) should be written. |
Write the value 0x0 to all addresses from 0x100 to 0x200:
|
|||
Write memory to an address range from Address1 to (Address1 + Address2) |
|
The command is used to specify a range of addresses (from Address1 to (Address1 + Size)) where the value(s) should be written. |
Write 0xFF to addresses from 0x300 to 0x350:
|
|||
Write memory to a variable |
|
The command is used to use a variable name to modify the memory at its address. |
Write two bytes (0xab, 0xa2) to the address of variable counter:
|
|||
Write memory using specifiers |
|
The command specifies the size or endianness of the values being written. Specifiers affect all values given in arguments following the specifier. Size specifiers include: •%Byte - 1 byte •%Short - 2 bytes •%Long - 4 bytes •%Quad - 8 bytes Endianness specifiers include: •%LE - Little endian •%BE - Big endian |
Write 4 bytes (Long type) to address 0x111 in default CPU endian:
Write 4 bytes (Long type) to address 0x111 in big endian:
|
|||
Write memory using value |
|
The command specifies the data to be written to the specified memory location(s). |
Write four bytes (0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF) to memory address 0x200:
Write two bytes (0xDE, 0xAD) + 2*2 bytes (0x00DE, 0x00AD) to memory address 0x200:
|
|||
Write memory using a string |
|
The command specifies the data in a form of characters to be written to the specified memory location(s). |
Write 4 bytes (ASCII values of characters) + 1 byte (0x0) to memory address 0x200:
|
|||
Modify Expression |
|
The command assigns a new value (R-value) to a modifiable storage location (L-value). The L-value can be a variable, array element, dereferenced pointer, structure member, register, absolute memory address, or I/O module pin. For more details, refer to Watch Expressions. |
Set varA to varB + 3:
Set register R13 to 3:
|
|||
Evaluate Expression |
|
The command retrieves and prints the value of a specified expression (R-value). This can be a variable, register, memory address, or an evaluated expression. For more details, refer to Watch Expressions. |
Print the value of varA:
Print the value of register R11:
|
Scripts and tools
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Execute Python file |
|
The command executes a Python script specified by <PythonFile>. The file path can be relative (from the workspace directory) or absolute (full path). If the file path contains spaces, it must be enclosed in double quotes (""). For more details, refer to Running Python scripts in winIDEA. |
Execute my_script.py in the workspace directory:
Execute the script located at C:\scripts\test.py:
Execute the script at C:\My Scripts\script.py (path with spaces):
|
||||
Execute script |
|
The command executes a predefined script identified by <ScriptName>, as listed in Tools | External Scripts or Tools | SoC Scripts. If the script name contains spaces, it must be enclosed in double quotes (""). |
Execute the script named my_script:
Execute the script named Custom Script:
|
||||
Execute Tool |
|
The command runs a tool identified by <ToolName>, as configured in Tools | Customize | Tools. If the tool name contains spaces, it must be enclosed in double quotes (""). For more details, refer to Customizing a shortcut to run a script. |
Execute the tool named MyCustomTool:
Execute Executes the tool named Advanced Tool:
|
Miscellaneous
Command |
Command prototype |
Description |
Example |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Add variable to Watch window |
|
The command adds a variable (<Variable>) to the default Watch window. |
Add the variable iCounter to the default Watch window:
|