emuSync
In this topic:
Introduction
The emuSync application offers coordinate use of multiple winIDEA Workspaces, synchronously starting and stopping parallel SoCs under winIDEA control. To open emuSync, go to Test | Launch emuSync.
EmuSync allows you to:
•Keep track of the many different winIDEA application controlling each SoC
•Provide shorthands to operations that are commonly performed in all SoCs at once (download, start, etc.)
•Automate synchronous starts and stops
When using emuSync, a list of winIDEA Workspaces is specified, where each can be in Master or Slave Mode. Stopping the Master Workspace causes all Slave Workspaces to stop. Optionally, all Slave Workspaces can be started when the Master Workspace runs. emuSync can load and save different configurations.
emuSync is a single window application divided into four parts:
•Configuration
•Instance workspaces
•Selected Instance
•All Instances

Configuration
The Configuration section displays the path to the active configuration file. The "..." button displays a pop-up menu with file commands: New, Open, Save, Save as.
•Always on top - When checked keeps the emuSync window above all other windows.
Configuration information is saved into text files with the .emuSync extension, which can be manually edited. The file is created automatically when you start a new configuration and is saved in a location of your choosing. The file includes three main sections:
•Configuration - This is where the selected winIDEA Workspaces are specified (wsPath field) and their operation mode (opMode field: master/slave) is defined.
•Logging - If the “enable” field is set to true, the logging menu appears in the emuSync main menu bar. There you can select the desired logging level and open the folder containing the log files.
•Module - Each of the available hooks has its own specified file path (hookPath field), name of python hook start method/function (hookStart field), and an enable field (isActive).
Below is an example of a configuration file:
configuration: |
Instance Workspaces
Each line of the list displays the number ID of the instance, its Master and Slave mode, its status, and the path to the Workspace.
Status
Status |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Workspace not attached to a winIDEA process |
 |
winIDEA is not connected to the debugger |
 |
Core execution is halted |
 |
winIDEA instance is in the stop mode. |
 |
winIDEA instance is in the running mode |
 |
winIDEA instance is detached |
Selected Instance
Depending on the status of the Workspace different commands are available. To operate multiple winIDEA instances from the emuSync application, you need to launch them first.
•Launch - Launch a new winIDEA instance and attach to it.
•Close - Close winIDEA instance.
•Attach - Attach to an open winIDEA instance or open one if no suitable instance is found.
•Detach - Detach/disconnect from winIDEA instance.
•Run - Start/continue core execution.
•Stop - Stop core execution.
•Download - Download files to the target CPU.
•Reset - Trigger a reset on the core.
•Master / Slave radio buttons- Toggle between the modes.
All Instances
The command buttons available in the Selected Instance section are duplicated here, but they operate on all instances at the same time. The checkboxes on the bottom are global options.
•Run slaves when master runs - If enabled, the Master Workspace entering running status causes all Slaves to run.
•Close all on exit - If enabled causes all associated winIDEA applications to be closed when emuSync is closed.
Options
There are additional options available in the application's menu bar:
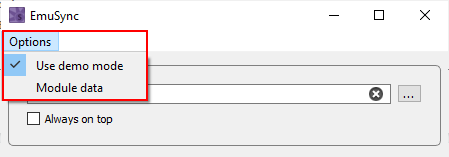
•Use Demo mode - Toggle Demo mode across all winIDEA instances.
•Module data - Provide a quick overview of the module and hook-related settings in the currently loaded configuration file. To edit these settings, edit the configuration file itself and then reload it in the emuSync application.
Hooks
emuSync allows you to implement custom Python hooks (or scripts) and run them according to the selected command. Hook paths and starting methods for each of the supported events are defined in the configuration emuSync file. If a specific hook is enabled in the configuration file, then it will be executed every time the specific command is given to a winIDEA instance.
Supported events
•onDownload (after Download)
•onReset (after Reset)
•onRun (after Run)
•onStop (after Stop)
•preDownload (before Download)
•preReset (before Reset)
•preRun (before Run)
•preStop (before Stop)
Requirements
The only requirement for a hook is that it can be passed an instance of the ConnectionMgr class. This enables you to create any of the other classes and managers available in winIDEA SDK and manipulate winIDEA instances. No logging handler is passed, so you must implement your own logging solution if needed.
More resources
•Multi-Core and Multi-SoC Synchronization - Overview
•Implement a custom emuSync Hook - How-to guide

